Unveiling The Differences In Effects Of Various Psychedelics, A Scientific Study
I recently read a research paper from Nature.com, Comparative Acute Effects Of Mescaline, Lysergic Acid Diethylamide, And Psilocybin In A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Cross-Over Study In Healthy Participants that confirmed something I had said for years based on my personal experience.
I’ve always believed that all tryptamines exhibit similar behaviors in small doses, and as I gained more experience with different psychedelics, I expanded that belief to include all psychedelics in small doses. Some people disagreed with me, but this study appears to provide support for my claims. I’m absolutely thrilled that science has validated my personal experiences! It’s a major leap forward in our comprehension of psychedelics, and it holds the potential to unlock new possibilities for treating mental health conditions. I’m filled with excitement as I eagerly await what the future has in store for this groundbreaking research.
The research conducted involved a cohort of 32 meticulously screened healthy participants, comprising both males and females. The primary objective of the study was to comprehensively examine the similarities and dissimilarities among several psychedelics, namely LSD, psilocybin, mescaline, DMT, and ayahuasca.
Under the guidance of a dedicated research team, the study employed a combination of participant-reported subjective experiences, objective measurements, and psychological assessments to undertake a comparative analysis of the acute effects induced by the various psychedelics. By administering psychoactive-equivalent doses and incorporating placebo formulations as control measures, the study provides scientific substantiation for the individual’s assertion that small doses of psychedelics manifest comparable behaviors.
The implications of these research findings are substantial for advancing our understanding of psychedelics and exploring their potential therapeutic applications within the realm of mental health treatments. Significantly propelling psychedelic research forward, this study bears the potential to lay the foundation for future breakthroughs and innovative interventions. The individual expresses enthusiasm regarding the future prospects of this research and its potential to make a profound impact on mental health conditions.
Conclusion
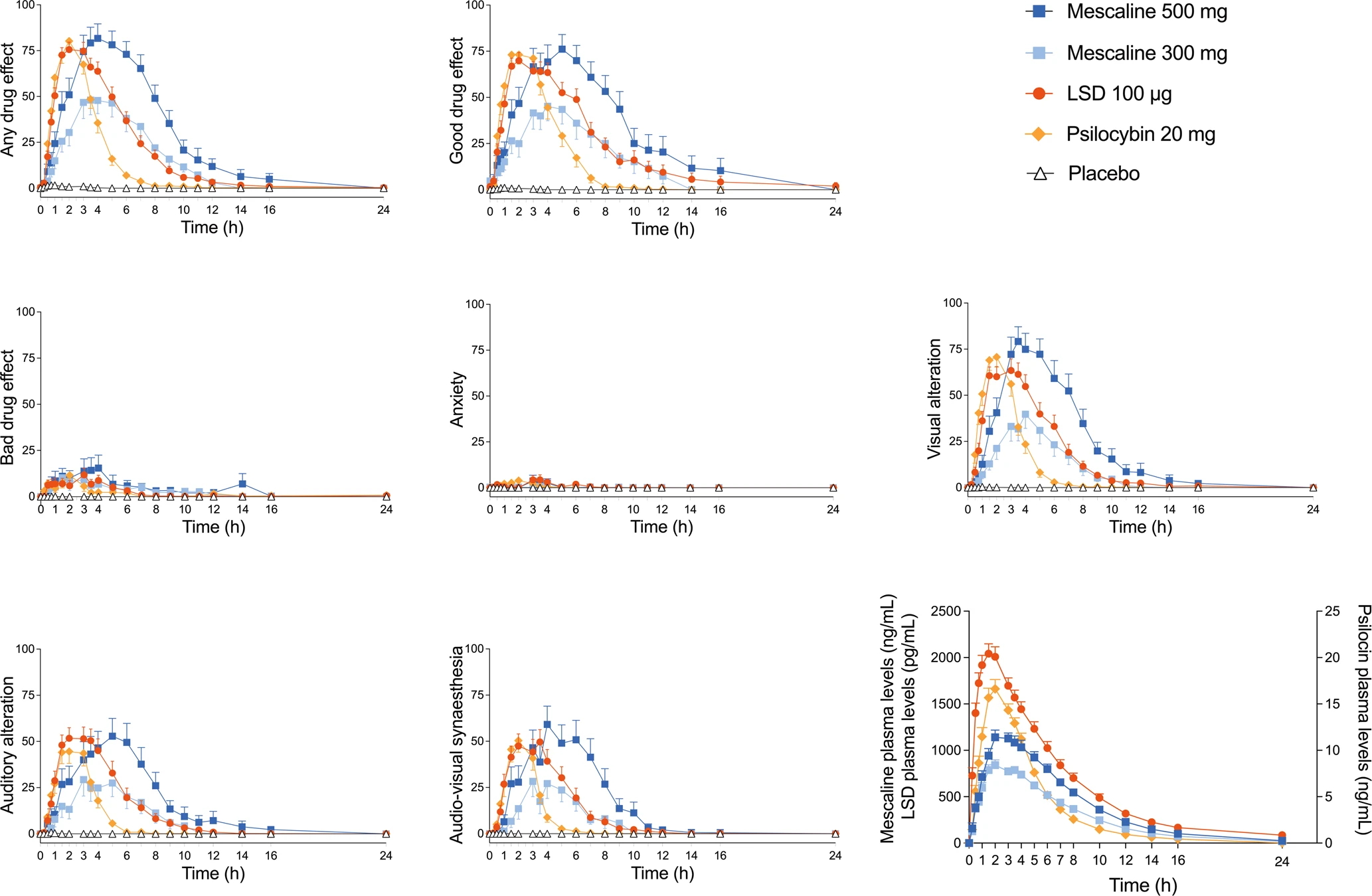
From: Comparative acute effects of mescaline, lysergic acid diethylamide, and psilocybin in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study in healthy participants
This groundbreaking study aimed to compare the altered states of consciousness induced by mescaline, LSD, and psilocybin— the classic psychedelics. The researchers found no significant qualitative differences in the subjective experiences and perceptions among these substances, suggesting that they elicit similar types of experiences in terms of their qualitative nature. However, there were notable disparities in the durations of action for each psychedelic, attributable to their distinct pharmacokinetic properties. This understanding is crucial for designing research protocols and optimizing psychedelic-assisted therapy.
The study’s findings have important implications for both research and psychedelic-assisted therapy. Researchers can benefit from this knowledge by designing protocols that align with the desired duration of the altered state, enhancing the consistency and predictability of their studies. In the context of therapy, the duration of the psychedelic experience plays a critical role in therapy sessions and the integration of the experience afterward. By recognizing the overlapping qualitative effects and considering the differences in durations of action, therapists can tailor treatment approaches to specific therapeutic goals and individual needs.
These findings emphasize the significance of dose finding in psychedelic research and therapy. Establishing appropriate dosage ranges for each psychedelic enables the development of standardized protocols that ensure consistent and predictable effects. This is essential for maintaining safety and optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
The study’s insights regarding dose ranges and qualitative similarities can guide clinicians in selecting the most suitable psychedelic substance for specific therapeutic purposes, facilitating personalized treatment approaches. By deepening our understanding of these psychedelics, responsible and effective utilization in therapeutic contexts can be promoted, benefiting individuals seeking personal growth, healing, and transformative experiences.


































